Abstract
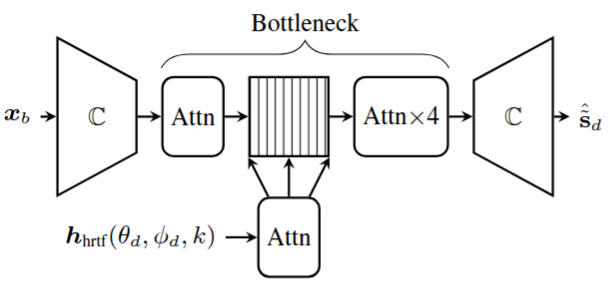
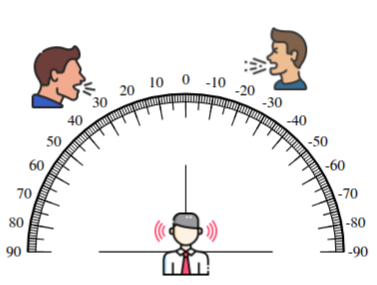
In this work, we address the problem of binaural target-speaker extraction in the presence of multiple simultaneous talkers. We propose a novel approach that leverages the individual listener’s Head-Related Transfer Function (HRTF)to isolate the target speaker. The proposed method is speaker-independent, as it does not rely on speaker embeddings. We employ a fully complex-valued neural network that operates directly on the complex-valued Short-Time Fourier transform (STFT) of the mixed audio signals, and compare it to a Real-Imaginary (RI)-based neural network, demonstrating the advantages of the former. We first evaluate the method in an anechoic, noise-free scenario, achieving excellent extraction performance while preserving the binaural cues of the target signal. We then extend the evaluation to reverberant conditions. Our method proves robust, maintaining speech clarity and source directionality while simultaneously reducing reverberation. A comparative analysis with existing binaural Target Speaker Extraction (TSE) methods shows that the proposed approach achieves performance comparable to state-of-the-art techniques in terms of noise reduction and perceptual quality, while providing a clear advantage in preserving binaural cues.
_elev_tensor([0]).png)
_elev_tensor([-10]).png)
_elev_tensor([0]).png)
_elev_tensor([0]).png)
_elev_tensor([0]).png)
_elev_tensor([10]).png)
_elev_tensor([0]).png)
_elev_tensor([-10]).png)